Calculation of probability (risk) vs odds In statistics, odds are an expression of relative probabilities, generally quoted as the odds in favor The odds (in favor) of an event or a proposition is the ratio of the probability that the event will happen to The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio) Let's look at an example Relative Risk/Risk Ratio Suppose you have a school that wants to test out a new tutoring program The New England Revolution look to extend their win streak Sunday against CF Montreal Sitting at No 1 in the Eastern Conference and No 2 in MLS standings, the Revs are coming off a 50 rout of Inter Miami CF on the road Wednesday CF Montreal is 644 and looks to bounce back after a 10 loss to

Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training
Which is better odds ratio or relative risk
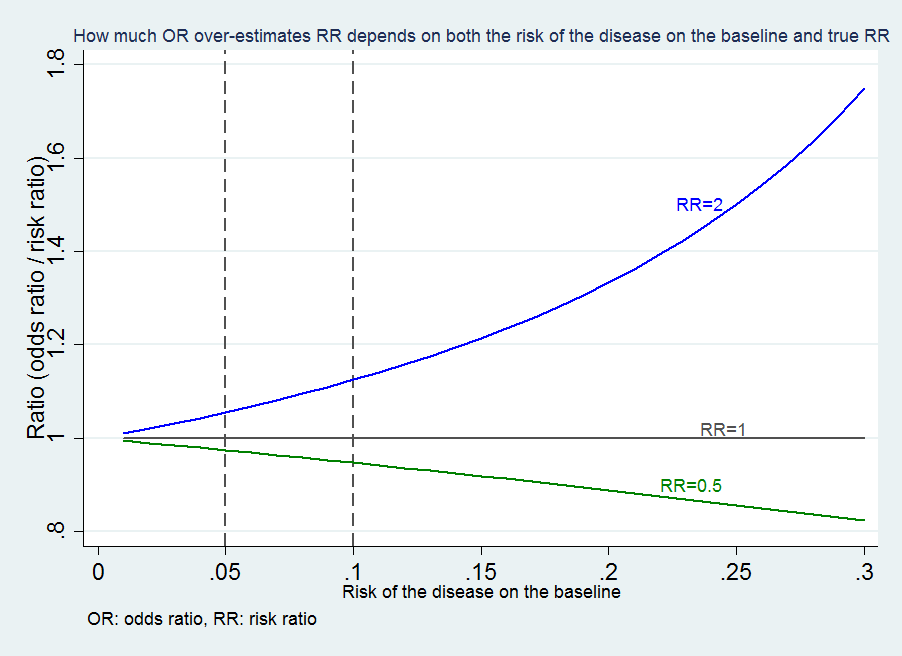
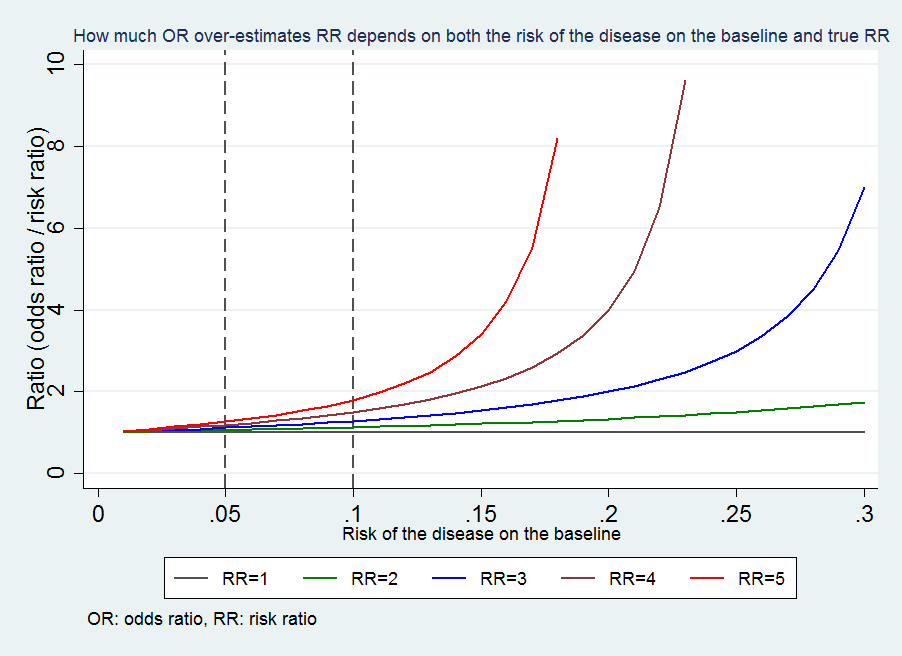
Which is better odds ratio or relative risk- Risk Ratio vs Odds Ratio Whereas RR can be interpreted in a straightforward way, OR can not A RR of 3 means the risk of an outcome is increased threefold A RR of 05 means the risk is cut in half But an OR of 3 doesn't mean the risk is threefold;The more common the disease, the larger is the gap between odds ratio and relative risk In our example above, p wine and p no_wine were 0009 and 0012 respectively, so the odds ratio was a good approximation of the relative risk OR = 0752 and RR = 075 If the risks were 08 and 09, the odds ratio and relative risk will be 2 very different numbers OR = 044 and RR = 0 Relative risk vs Odds




Odds Ratio Article
Probability is a branch of mathematics, which includes odds One can measure chance, with the help of odds or probability While odds are a ratio of occurrence to nonoccurrence, the probability is the ratio of occurrence to the wholeEnglishwise, they are correct it is the odds and the odds are based on a ratio calculation It is not, however, the odds ratio that is talked about when results are reported The odds ratio when results are reported refers to the ratio of two odds or, if you prefer, the ratio of two odds ratios That is, let us write o(Xb) = exp(Xb)2) Calculate the odds of exposure in cases and noncases 3) Calculate the odds ratio using the crossproduct ratio 4) How does the difference between the two prevalences of breast cancer (75% vs 25%) compare to the odds ratio?
Odds Ratio (OR) is a measure associations between exposure (risk factors) and the incidence of disease;Relative Risk, Odds, and Fisher's exact test I) Relative Risk A) Simply, relative risk is the ratio of p 1/p 2 For instance, suppose we wanted to take another look at our Seat belt safety data from Florida Safety equipment Injury in use Fatal Nonfatal Total None 1,601 165,527 167,128 Seat belt 510 412,368 412,878Rangers vs Tigers odds, line 21 MLB picks, predictions for July 22 from proven computer model (risk $135 to win $100)
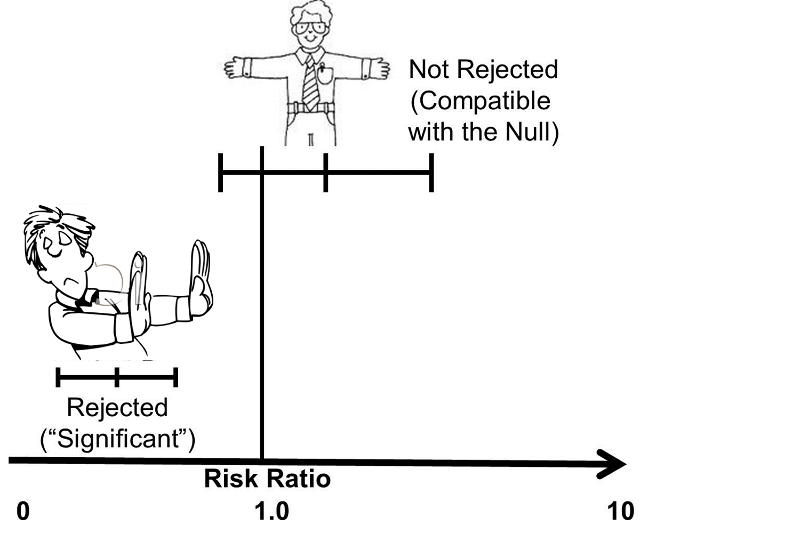
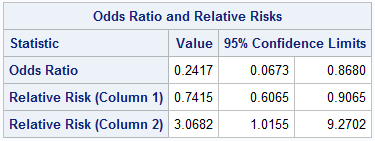
Abstract Odds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR)In clinical studies, as well as in some other settings, the parameter of greatest interest is often the relative risk rather than the odds ratio The relative risk is best estimated using a population sample, but if the rare disease assumption holds, the odds ratio is a good approximation to the relative risk — the odds is p / (1 − p), so when p moves towards zero, 1 − p moves towards 1Relative risk, the odds ratio is said to be significant if the confidence interval does not include 1 In this example the upper and lower limit of the 95% CI are both greater than 1 so the odds of death are said to be significantly higher in the control group and the result is reported as OR 3;




How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence
9221 Risk and odds In general conversation the terms 'risk' and 'odds' are used interchangeably (as are the terms 'chance', 'probability' and 'likelihood') as if they describe the same quantity In statistics, however, risk and odds have particular meanings and are calculated in different ways When the difference Washington Cancer Patients Found To Be At Greater Risk For Bankruptcy Than People Without A Cancer Diagnosis Health Affairs (Project Hope), 32(6), 1143–1152 Bureau of Labor Statistics, EmployerReported Workplace Injuries and Illnesses (Annual) 16, Table1 Incidence rates of nonfatal occupational injuries and illnesses by industry and case95% CI (143, 616) Steps in SPSS




Solved Look At Slide 25 In The Descriptive And Inferentia Chegg Com




Odds Ratio Http Www Slideshare Net Terryshaneyfelt7 What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean Statistics Math Research Methods Academic Research
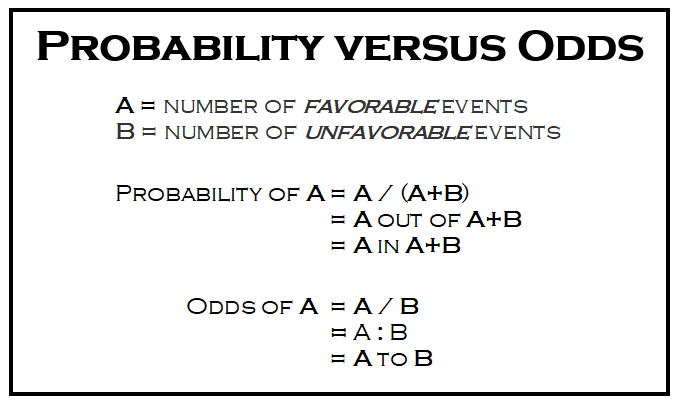
Odds can be expressed as a ratio of the probability an event will happen divided by the probability an event won't happen Odds in favor of A = A / (1 A), usually simplified to lowest terms, For instance, if the probability of an event occurring is 075, then the odds for it happening are 075/025 = 3/1 = 3 to 1 for, while the probability that it doesn't occur is 1 to 3 againstBecause in statistics odds are converted to the 'to one' standard we need to think about how we can consider the odds in favour of surviving which at present is none_death to deaths = 1 to nine = 19 = 1/9 = to convert this to the 'to one' standard we just divide each by the denominator (ie 9) so now we have the ratio of• The risk of sexual dysfunction with venlafaxine is 24 times that with placebo • The risk of sexual dysfunction with venlafaxine is 240% that with placebo • Venlafaxine is associated with a 14fold increase in the risk of sexual dysfunction • Venlafaxine is associated with a 140% increase in the risk of sexual dysfunction




Statistics Basics Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Calculation In Excel Bi Practice




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Risk Difference Statistics Tutorial 30 Marinstatslectures Youtube
Odds The National Safety Council compiled an oddsofdying table for 08, which further illustrates the relative risks of flying and driving safety It calculated the odds of dying in a motorA general rule is that when the prevalence of the disease isOdds and Odds Ratios Odds are the probability of an event happening / the probability of an event not happening Thus the odds of throwing a three with one die is 1/5 odds = probability / (1 probability) and conversely probability = odds / (1 odds) Odds Ratio Odds ratio is the ratio of odds for the exposed group vs the unexposed group




Understanding Systematic Reviews And Meta Analysis Archives Of Disease In Childhood
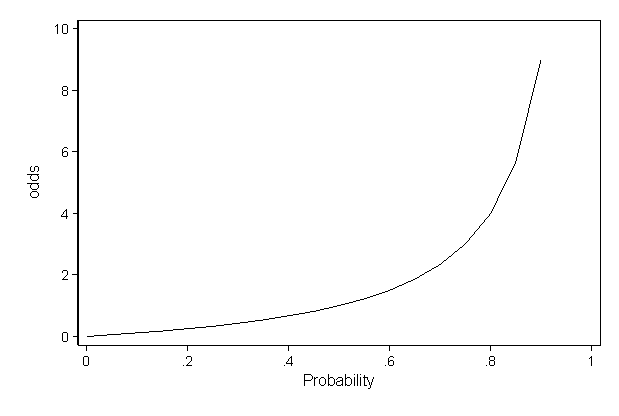



Faq How Do I Interpret Odds Ratios In Logistic Regression
The risk or odds ratio is the risk or odds in the exposed group divided by the risk or odds in the control group A risk or odds ratio = 1 indicates no difference between the groups A risk or odds ratio > 1 indicates a heightened probability of the outcome in the treatment group The two metrics track each other, but are not equalLifetime odds of death for selected causes, United States, 19;Cause of Death Odds of Dying;




Odds Ratio Wikipedia




Odds Ratio Article
The annual risk of being killed in a plane crash for the average American is about 1 in 11 million On that basis, the risk looks pretty small Compare that, for example, to the annual riskRelative Risk and Odds Ratio Calculator This Relative Risk and Odds Ratio calculator allows you to determine the comparative risk of the occurrence of a significant event (or outcome) for two groups For example, suppose the members of one group each eat a kilo of cheese every day, and the members of another group eat no cheese, and you haveThe odds ratio is always positive, although the estimated log odds can be positive or negative (log odds of −02 equals odds ratio of 0 = exp(−02)) The odds ratio for a risk factor contributing to a clinical outcome can be interpreted as whether someone with the risk factor is more or less likely than someone without that risk factor
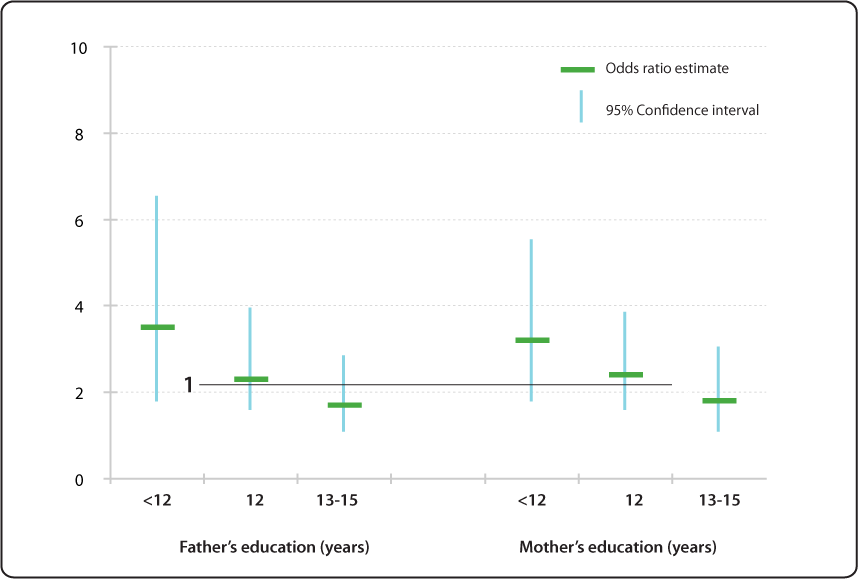



Relative Risk Odds Ratio Estimate With 95 Confidence Intervals Of Children Having Specific Language Impairment Sli By Parent S Level Of Education Reference College Graduate Or More Education 16 Years Nidcd




Attributable Risk And Odds Ratio Online Medical Library
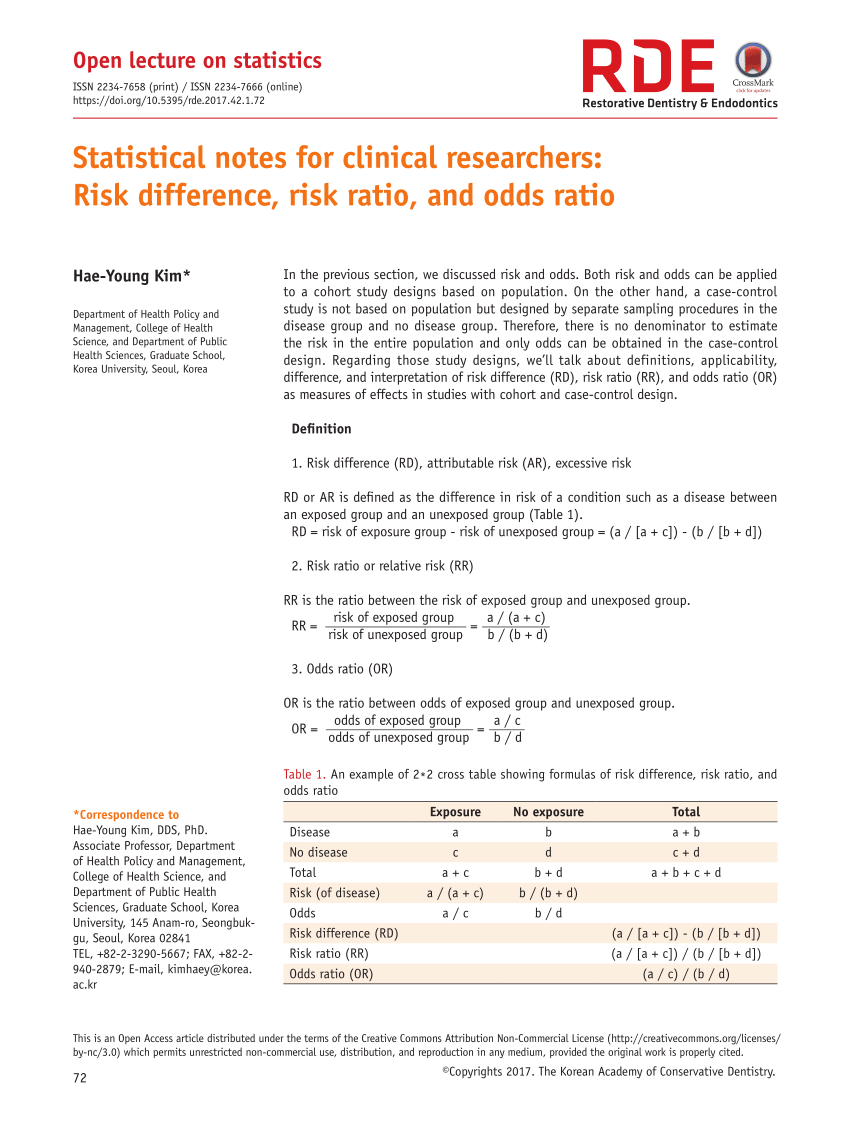
Calculated from the incidence of the disease in at risk groups (exposed to risk factors) compared to the incidence of the disease in nonrisk group (not exposed to a risk factor) The probability that an event will occur is the fraction of times you expect to see that event in many trials Probabilities always range between 0 and 1 The odds are defined as the probability that the event will occur divided by the probability that the event will not occur If the probability of an event occurring is Y, then the probability of the event not occurring is 1Y (Example If the probability of an event is 080 (80%), then the probabilityIf the outcome is rare in both exposed and unexposed persons, the odds ratio (A/B/C/D) will approximate the risk ratio (A/(A B)/C/(C D)) However, when the study outcome is common and the risk ratio is not close to 1, the odds ratio will be further from 1 compared with the risk ratio




Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training
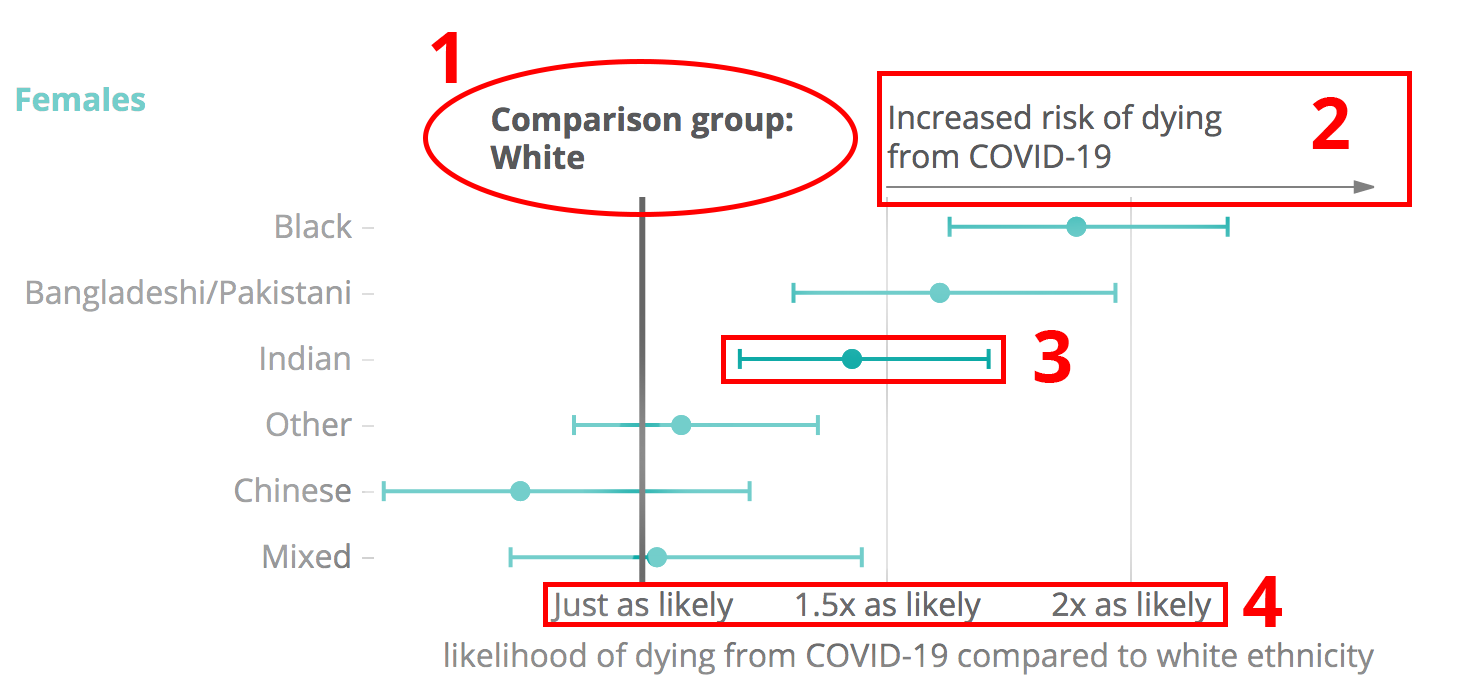



Against All Odds How To Visualise Odds Ratios To Non Expert Audiences Henry Lau
Rather the odds is threefold greater Interpretation of an OR must be in terms of odds, notIn the endocarditis example, the risk (or odds) of dying if treated with the new drug is relative to the risk (odds) of dying if treated with the standard treatment antibiotic protocol Relative risk assessment statistics are particularly suited to diagnostic and treatment decisionmaking and will be addressed in a future paper For most people currently being offered the OxfordAstraZeneca vaccine, the benefits clearly outweigh the risks But the UK's Joint Committee on Vaccination and Immunisation (JCVI) has recommended



Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios




Risks Of And Risk Factors For Covid 19 Disease In People With Diabetes A Cohort Study Of The Total Population Of Scotland The Lancet Diabetes Endocrinology
Odds Ratio (OR) measures the association between an outcome and a treatment/exposure Or in other words, a comparison of an outcome given two different groups (exposure vs absence of exposure) OR is a comparison of two odds the odds of an outcome occurring given a treatment compared to the odds of the outcome occurring without the treatmentAbout Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us CreatorsHow to find probability and odds and the difference between the two We also discuss experimental probablility, theoretical probability, odds in favor, and




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube
Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk When two groups are under study or observation, you can use two measures to describe the comparative likelihood of an event happening These two measures are the odds ratio and relative risk Both are two different statistical concepts, although so much related to each other1) 2) The odds of exposure in case group a/c = 75/25 = 3 control group b/d = 25/75 = 1/3 Comparing AstraZeneca vaccine bloodclot risk to odds of dying in a car crash unhelpful, experts say Downplaying the risk with inappropriate comparisons will not build coronavirus vaccine




Frontiers Odds Ratio Or Prevalence Ratio An Overview Of Reported Statistical Methods And Appropriateness Of Interpretations In Cross Sectional Studies With Dichotomous Outcomes In Veterinary Medicine Veterinary Science




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal
Risk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three common, but often misused, statistical measures in clinical research In this paper, the authors dissect what each of these terms define, and provide examples from the medical literature to illustrate each of these statistical measures Finally, the correct and incorrect methods to use these measures are summarized A betting odd opportunity should be considered valuable if the probability assessed for an outcome is higher than the implied probability estimated by the bookmaker Read more on the math behindAttack Rate (Risk) Attack rate for exposed = a ⁄ ab Attack rate for unexposed = c ⁄ cd For this example Risk of tuberculosis among East wing residents = 28 ⁄ 157 = 0178 = 178% Risk of tuberculosis among West wing residents = 4 ⁄ 137 = 0029 = 29% The risk ratio is simply the ratio of these two risks Risk ratio = 178 ⁄ 29 = 61



Risk Of Death By Age And Sex



Q Tbn And9gctxz8owky Sul84xtk4ggzacxwhkmhguhlxwyjj9avufagdrhwm Usqp Cau
1 hour ago First pitch is scheduled for 1010 pm ET Let's analyze BetMGM Sportsbook's lines around the Athletics vs Padres odds with MLB picks and predictions Season series Tied 00 RHP James Kaprielian is Oakland's projected starter Kaprielian is 53 with a 265 ERA (68 IP, ER), 112 WHIP, 34 BB/9 and 97 K/9 over 12 startsOdds (Safety) = 12/72 = 1787 Now get out your calculator, because you'll see how these relate to each other Odds (Accident) = Pr (Accident)/Pr (Safety) = 053/947 Understanding Probability, Odds, and Odds Ratios in Logistic Regression Despite the way the terms are used in common English, odds and probability are not interchangeableThe odds ratio can also be used to determine whether a particular exposure is a risk factor for a particular outcome, and to compare the magnitude of various risk factors for that outcome OR=1 Exposure does not affect odds of outcome OR>1 Exposure associated with higher odds of outcome OR



Risk Of Death By Age And Sex



Http Www Stat Colostate Edu Gumina St1 Pdf Categoricalanalysis Pdf
Converting Odds to Probability Simply add the 2 components of the odds together to make a new denominator, and use the old numerator eg If the odds are 35, or 3 to 5, the probability is 3 ÷ (35) = 3/8 = 375% Converting Probability to Odds Take the probability, and divide it by its compliment = (1itself) egHeart disease 1 in 6 Cancer 1 in 7 All preventable causes of death 1 in 24 Chronic lower respiratory disease 1 in 27 Suicide 1 in Opioid overdose 1 in 92 Fall 1 in 106 Motorvehicle crash 1 in 107 Gun assault 1 in 2 Pedestrian incident 1 in 543 Motorcyclist 1 in 9 Drowning"Odds" and "Risk" are the most common terms which are used as measures of association between variables In this article, which is the fourth in the series of common pitfalls in statistical analysis, we explain the meaning of risk and odds and the difference between the two




Medical Statistics Ix Bias Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Youtube
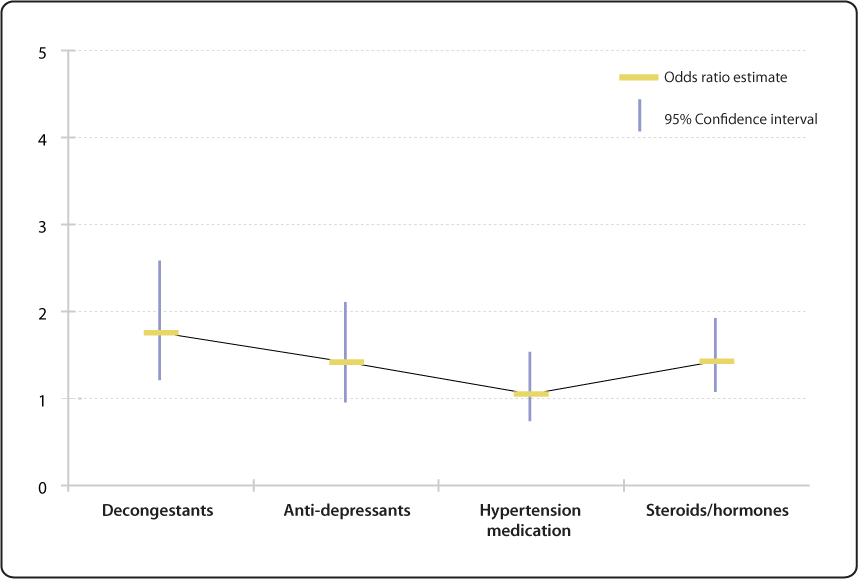



Relative Risk Odds Ratio Estimate With 95 Confidence Intervals For People To 66 Years Of Age With Current Medication Use Ever Having Voice Problems Or Disorders Nidcd
An odds ratio (OR) is a measure of association between an exposure and an outcome The OR represents the odds that an outcome will occur given a particular exposure, compared to the odds of the outcome occurring in the absence of that exposure odds are different to probability — odds is the ratio of the probability that the event of interest Odds ratio vs relative risk Odds ratios and relative risks are interpreted in much the same way and if and are much less than and then the odds ratio will be almost the same as the relative risk In some sense the relative risk is a more intuitive measure of effect size Note that the choice is only for prospective studies were the distinction For example an odds of 01 is written as 110 and an odds of 5 is written as 51 Risk and risk ratios are more commonly used than odds and odds ratios in medicine as these are much more intuitive Risk describes the probability of an event occurring




Risk Differences And Rate Differences



Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Interpreting Odds Ratio Senguptas Research Academy




The Binomial Applied Absolute And Relative Risks Chisquare



Orr Objective Response Rate And Related Statistics Part 2 Odds Ratio




Numerators Denominators And Populations At Risk Health Knowledge



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Measures Of Association Stats Medbullets Step 1




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence
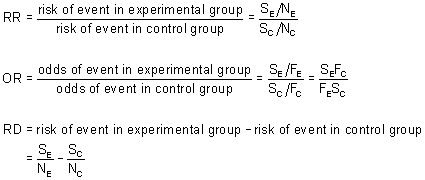



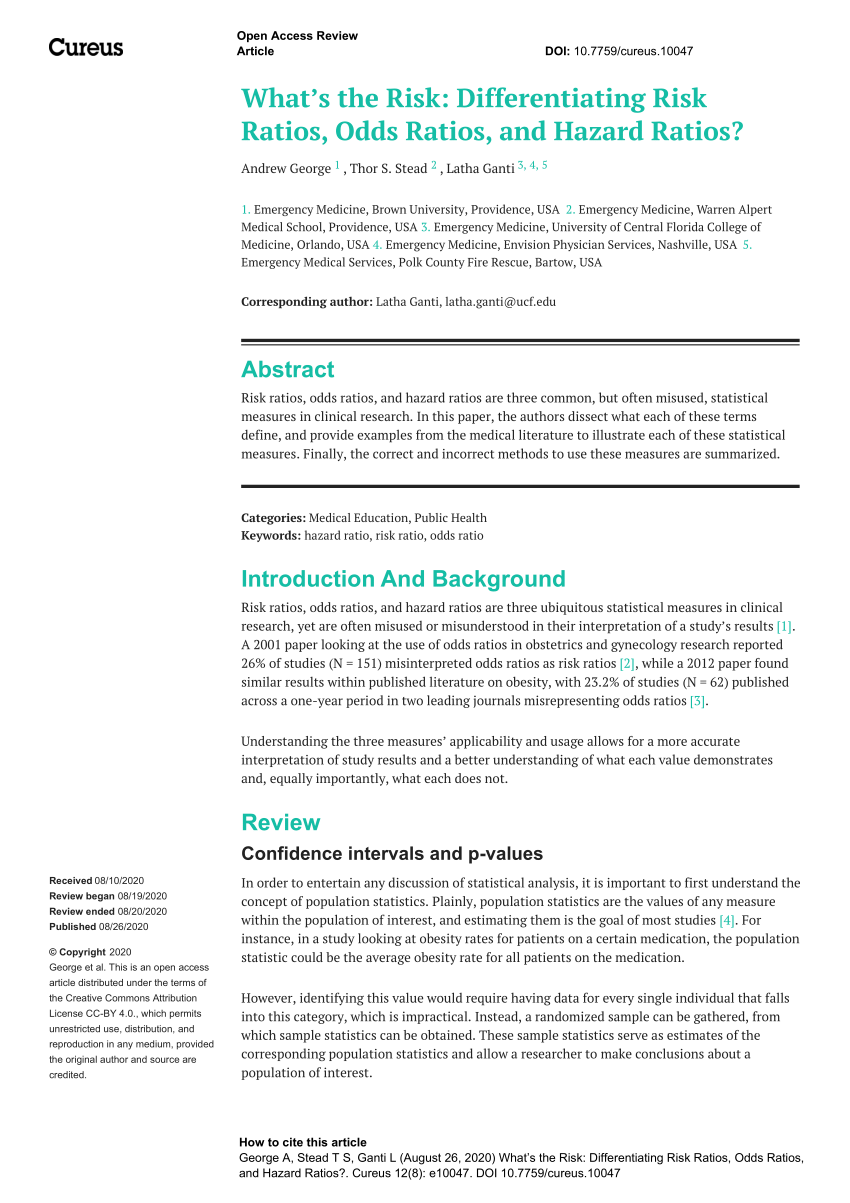
Box 9 2 A Calculation Of Rr Or And Rd




Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology
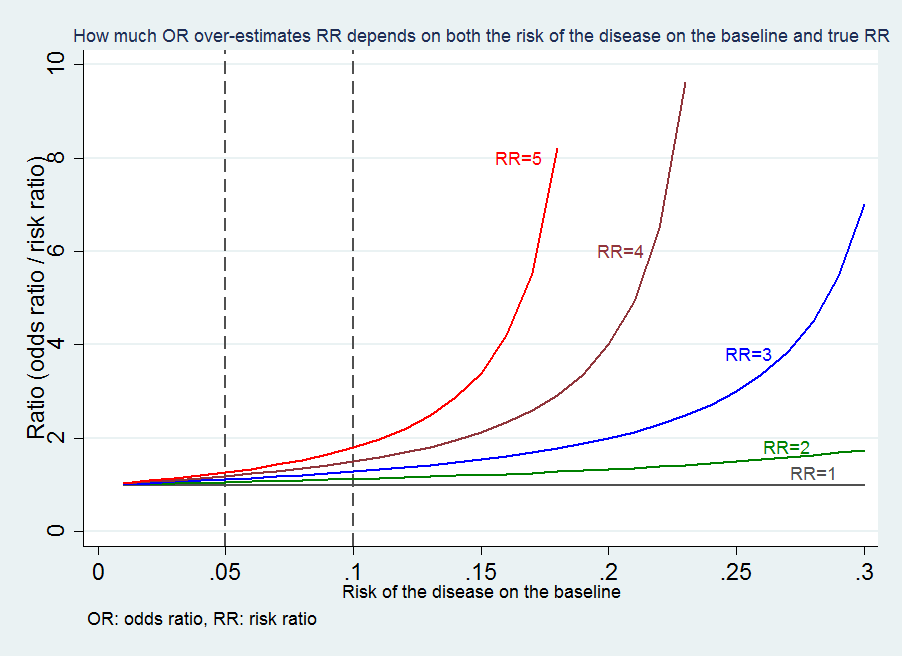



Medical Statistics And Data Science Statistics
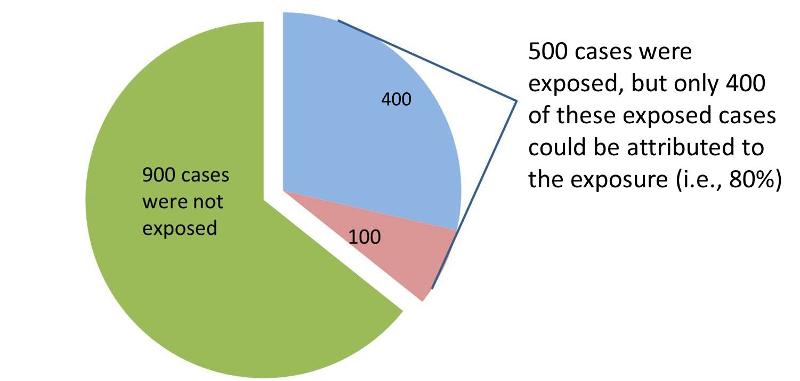



Measures Of Association



Medical Statistics And Data Science Statistics



1




How To Calculate An Odds Ratio Youtube



Http Www Floppybunny Org Robin Web Virtualclassroom Stats Basics Part13 Risks Rates Odds Pdf




Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals



Confidence Intervals And P Values



1



Q Tbn And9gcsdciarve4qxmues2ip Qg8ugk1mshcabjsxsnb3oitlp1asplq Usqp Cau
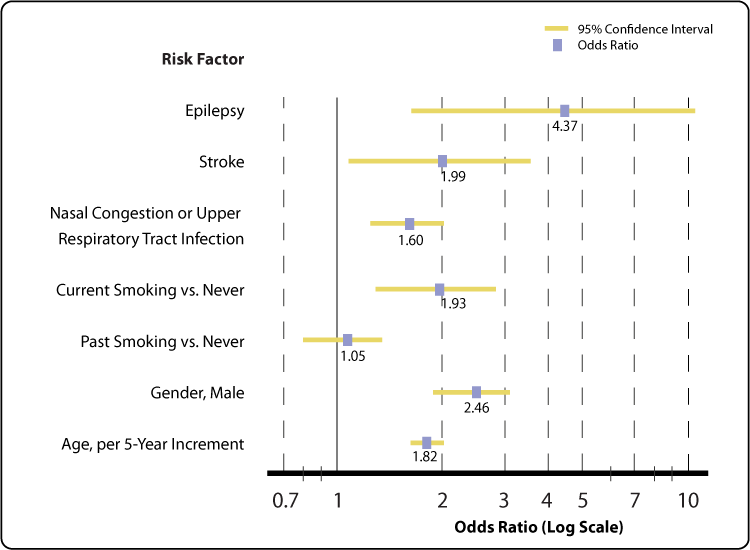



Selected Risk Factors For Smell Impairment Nidcd
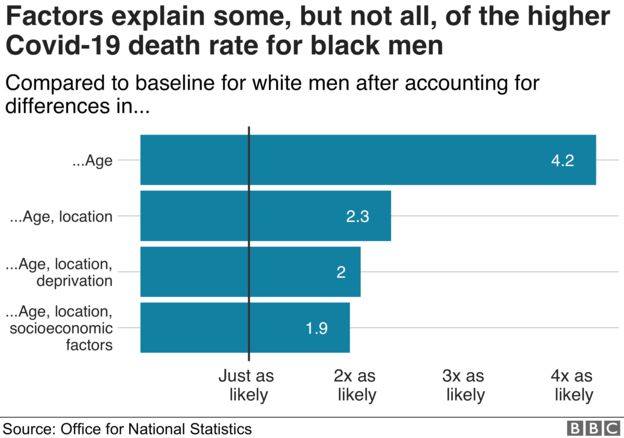



Against All Odds How To Visualise Odds Ratios To Non Expert Audiences Henry Lau
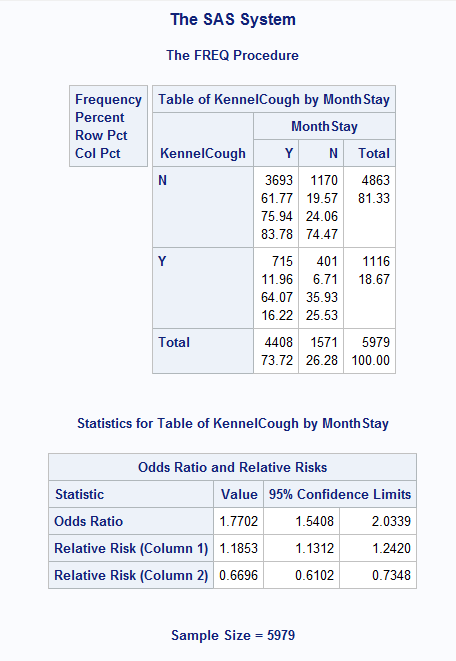



Different Odds Ratio From Proc Freq Proc Logisti Sas Support Communities
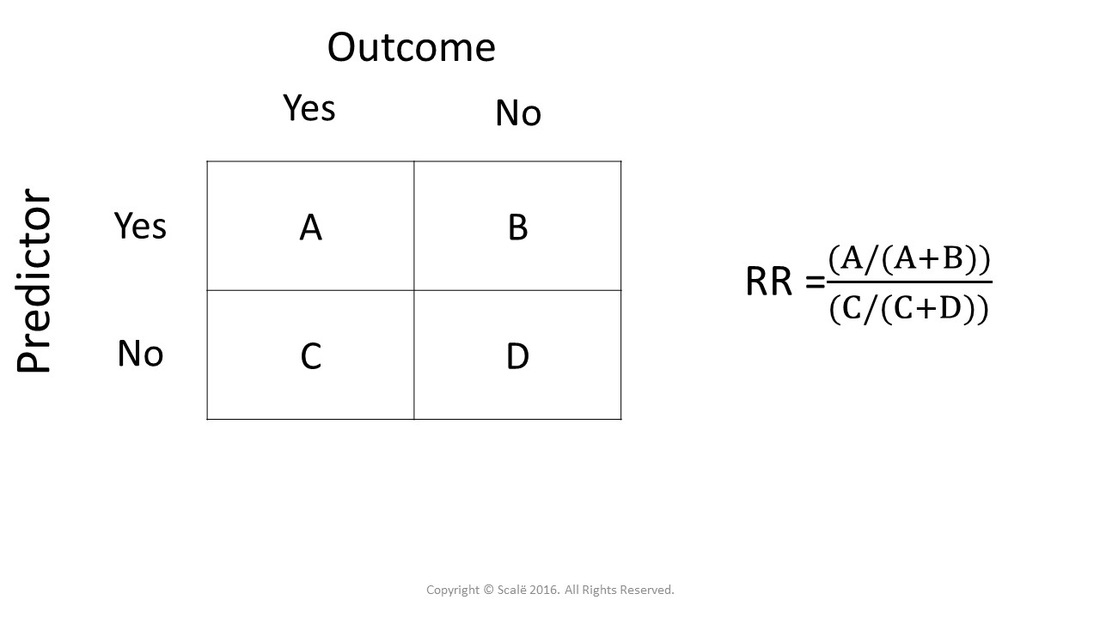



Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals




Forest Plot Showing Relative Statistics Of Odds Ratio A And B Or Download Scientific Diagram




Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Extensive Video Youtube
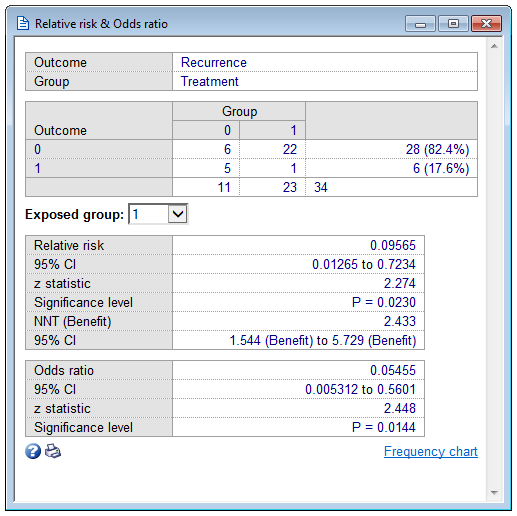



Relative Risk Odds Ratio




Rr Interpretation Http Www Slideshare Net Terryshaneyfelt7 What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean Statistics Math Research Methods Nursing Research




Pdf Common Pitfalls In Statistical Analysis Odds Versus Risk
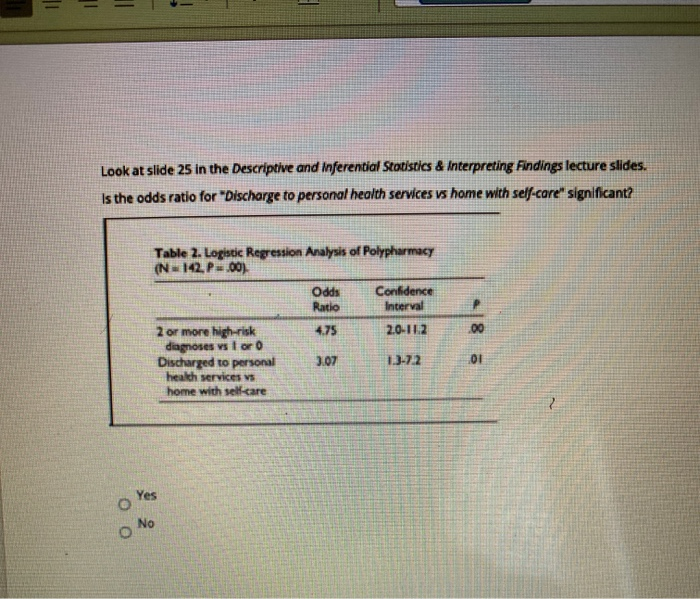



Look At Slide 25 In The Descriptive And Inferential Chegg Com
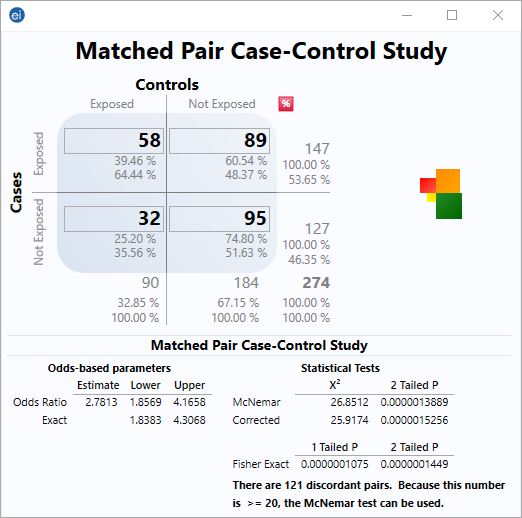



Matched Pair Case Control Statcalc User Guide Support Epi Info Cdc




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube




Statquest Odds Ratios And Log Odds Ratios Clearly Explained Youtube




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Statistics In Medicine Calculating Confidence Intervals For Relative Risks Odds Ratios And Standardised Ratios And Rates The Bmj




What Are The Odds Of Dying From Covid 19 Vs Lightning Wqad Com
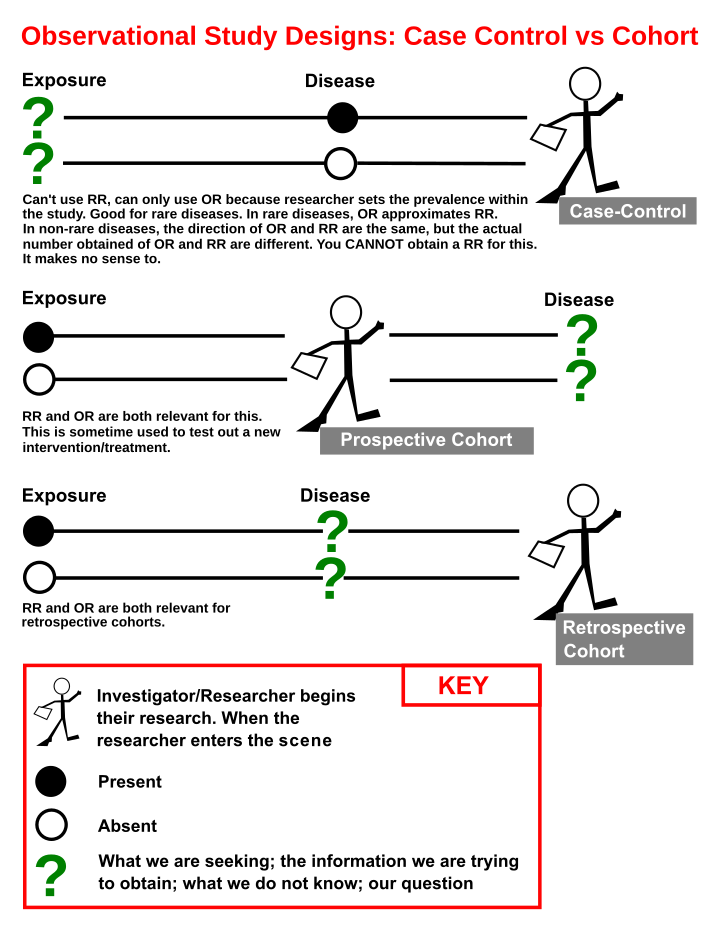



Cohort Statistics Wikiwand




Relative Risk Http Www Slideshare Net Terryshaneyfelt7 What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean Study Skills Statistics Math Research Methods




Relative Risk And Absolute Risk Definition And Examples Statistics How To



Ctspedia Ctspedia Oddsrisk




Statistics Part 13 Measuring Association Between Categorical Data Relative Risk Odds Ratio Attributable Risk Logistic Regression Data Lab Bangladesh




Relative Risk Wikipedia




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor
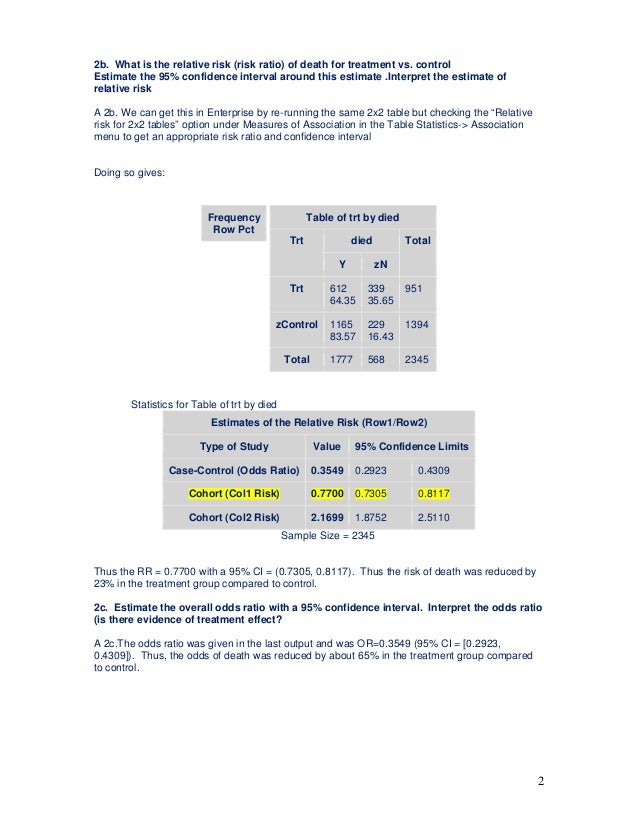



Testing Of Hypothesis Homework Help1



Research Statistics Basics Contents 1 Basic Concepts 2 References Basic Concepts Null Hypothesis The Hypothesis That The Independent Variable Has No Effect On The Dependent Variable For Example Steroids Do Not Improve Outcomes In Ards Would Be
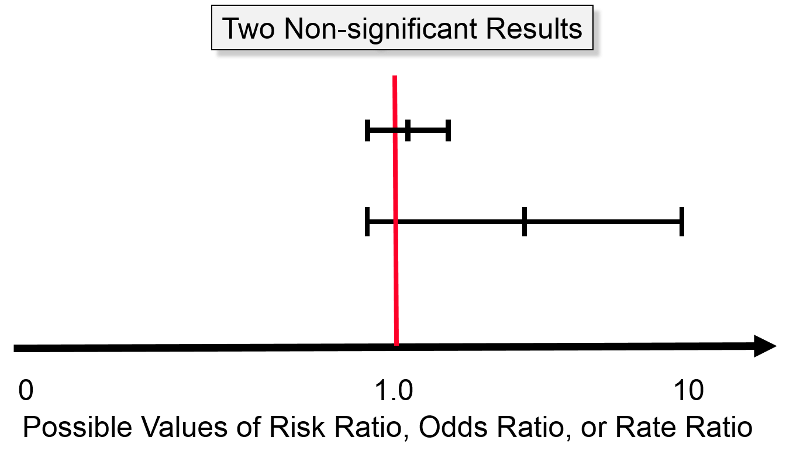



Confidence Intervals And P Values




Odds Ratio Wikipedia




Bi Practice Page 4 A Journey Of A Thousand Miles Begins With The First Step




Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk



What Are The Odds Stats With Cats Blog




Odds Ratio Calculation And Interpretation Statistics How To




Spss Video 10 Obtaining Odds Ratio Relative Risk In Spss Risk Lean Six Sigma Odds



Statistics Basics Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Calculation In Excel Bi Practice




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine




When Can Odds Ratios Mislead The Bmj




Statistics For Afp Dr Mohammad A Fallaha Afp




Statistics Part 13 Measuring Association Between Categorical Data Relative Risk Odds Ratio Attributable Risk Logistic Regression Data Lab Bangladesh



Pdf Statistical Notes For Clinical Researchers Risk Difference Risk Ratio And Odds Ratio




A Odds Ratio With Corresponding 95 Confidence Intervals For Download Scientific Diagram



Medical Statistics And Data Science Statistics
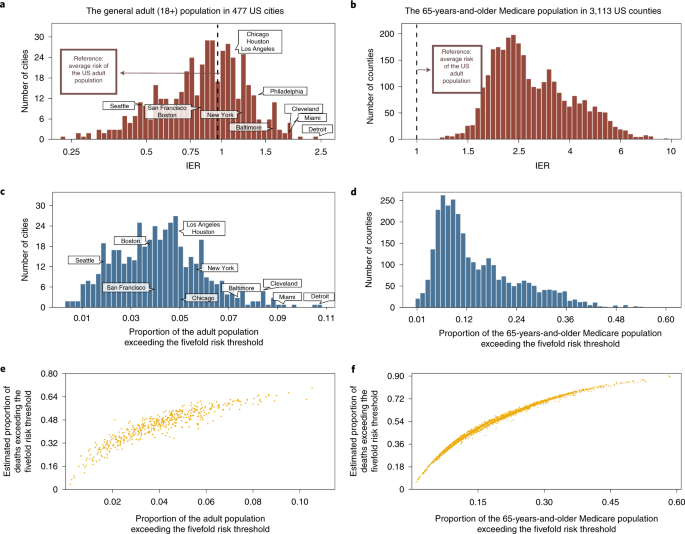



Individual And Community Level Risk For Covid 19 Mortality In The United States Nature Medicine



Odds Vs Risk Vantage Research




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
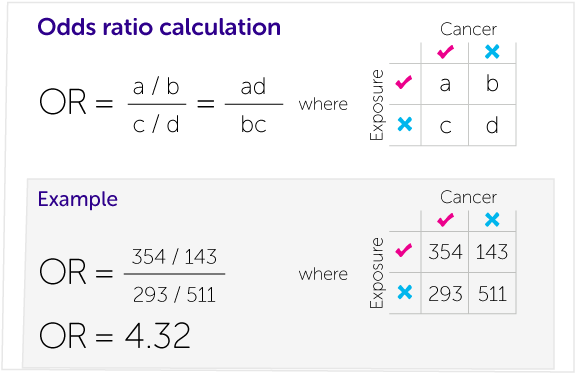



Our Calculations Explained Cancer Research Uk




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence
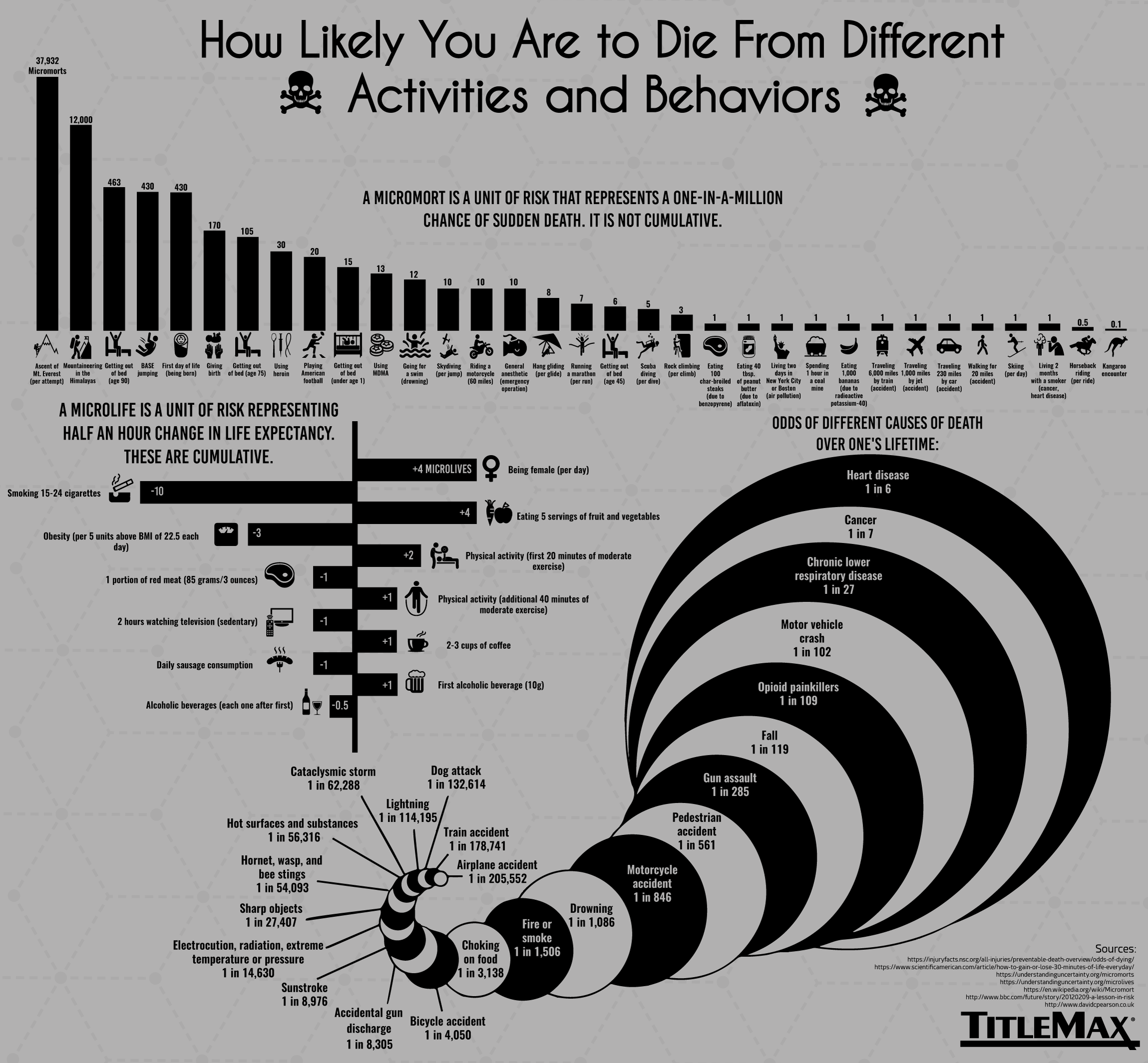



How Likely You Are To Die From Different Activities And Behaviors Infographic Article




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Risk Difference Statistics Tutorial 30 Marinstatslectures Youtube Study Skills Statistics Tutorial




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence
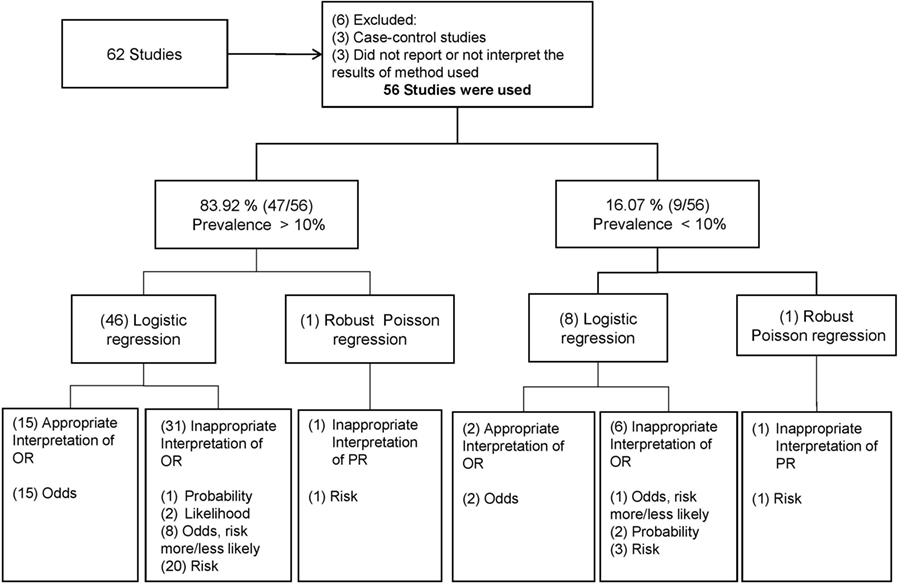



Frontiers Odds Ratio Or Prevalence Ratio An Overview Of Reported Statistical Methods And Appropriateness Of Interpretations In Cross Sectional Studies With Dichotomous Outcomes In Veterinary Medicine Veterinary Science




Rde Restorative Dentistry Endodontics




Odds Ratio Wikipedia




Medical Statistics Ix Bias Relative Risk And Odds Ratio
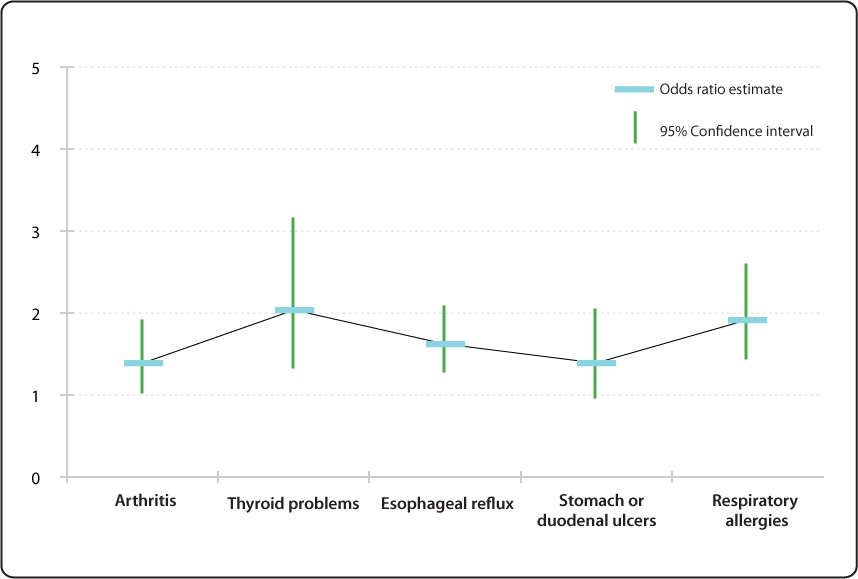



Relative Risk Odds Ratio Estimate With 95 Confidence Intervals For People To 66 Years Of Age And With Selected Conditions Ever Having Voice Problems Or Disorders Nidcd



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿